Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 K
K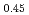 Li
Li )NbO
)NbO solid solutions by malic acid complex solution method
solid solutions by malic acid complex solution methodNakai, Tomoaki*; Kobune, Masafumi*; Nagamoto, Takeru*; Kikuchi, Takeyuki*; Yoneda, Yasuhiro
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 41(3), p.251 - 254, 2016/09
Solid solutions of NaNbO and KNbO
and KNbO are the candidate for non-Pb piezoelectric materials. It is difficult to obtain dense ceramics owing to the difference of their calcination temperature. We developed the malic acid complex method to obtain the (Na
are the candidate for non-Pb piezoelectric materials. It is difficult to obtain dense ceramics owing to the difference of their calcination temperature. We developed the malic acid complex method to obtain the (Na K
K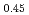 Li
Li )NbO
)NbO to obtain a high-quality ceramics sample. It was found that (Na
to obtain a high-quality ceramics sample. It was found that (Na K
K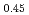 Li
Li )NbO
)NbO lies complicated phase boundaries; one is the structural phase boundary between NaNbO
lies complicated phase boundaries; one is the structural phase boundary between NaNbO and KNbO
and KNbO , the other is that between (Na,K)NbO
, the other is that between (Na,K)NbO mixture and LiNbO
mixture and LiNbO , which is a sintering additive.
, which is a sintering additive.
 Na
Na TiO
TiO , Bi
, Bi Na
Na Li
Li TiO
TiO , and 0.95Bi
, and 0.95Bi Na
Na TiO
TiO
 0.05BaMn
0.05BaMn V
V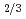 O
O
Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Nagamoto, Takeru*; Nakai, Tomoaki*; Kobune, Masafumi*
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 41(2), p.197 - 200, 2016/06
Bi Na
Na TiO
TiO (BNT) has been investigated as a lead-free piezoelectric material. We have already performed structure analysis of BNT. The average structure of BNT with low-temperature synthesis is a rhombohedral structure and it becomes a monoclinic structure as the synthesized temperature increases. Our local structure analysis indicated that the
(BNT) has been investigated as a lead-free piezoelectric material. We have already performed structure analysis of BNT. The average structure of BNT with low-temperature synthesis is a rhombohedral structure and it becomes a monoclinic structure as the synthesized temperature increases. Our local structure analysis indicated that the 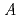 -site atoms of Bi and Na displaced toward different position depending on the lattice expansion and construction. We synthesized BNT crystals with various substitution and performed local structure analysis to examine the hypothesis. The local structure analysis revealed that the substitution effect on BNT can be explained by our hypothesis.
-site atoms of Bi and Na displaced toward different position depending on the lattice expansion and construction. We synthesized BNT crystals with various substitution and performed local structure analysis to examine the hypothesis. The local structure analysis revealed that the substitution effect on BNT can be explained by our hypothesis.
Ishikawa, Norito; Okubo, Nariaki; Taguchi, Tomitsugu
no journal, ,
In this study, CeO was irradiated with 200 MeV Au ions at oblique incidence. Observation of as-irradiated samples by transmission electron microscope (TEM) shows that hillocks are created not only at the wide surfaces, but also at the side faces of the thin samples. Since the hillocks created at the side faces can be imaged by TEM, their shape and crystallographic features can be revealed. From the images of hillocks created at the side faces, many of the hillocks are found to be spherical. We present an experimental evidence that hillocks created for CeO
was irradiated with 200 MeV Au ions at oblique incidence. Observation of as-irradiated samples by transmission electron microscope (TEM) shows that hillocks are created not only at the wide surfaces, but also at the side faces of the thin samples. Since the hillocks created at the side faces can be imaged by TEM, their shape and crystallographic features can be revealed. From the images of hillocks created at the side faces, many of the hillocks are found to be spherical. We present an experimental evidence that hillocks created for CeO irradiated with swift heavy ions have a crystal structure whose lattice spacing and orientation coincide with those of the matrix. The present method1) of observing hillocks can be a complementary technique to AFM(Atomic Force Microscopy.
irradiated with swift heavy ions have a crystal structure whose lattice spacing and orientation coincide with those of the matrix. The present method1) of observing hillocks can be a complementary technique to AFM(Atomic Force Microscopy.
Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Kimura, Atsushi; Idesaki, Akira; Ishii, Yasuyuki; Yamada, Naoto; Koka, Masashi; Shimada, Akihiko; Okubo, Takeru; Sato, Takahiro; Taguchi, Mitsumasa
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yamaguchi, Masatake; Ebihara, Kenichi; Itakura, Mitsuhiro
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 films using electron beams and
films using electron beams and  -rays
-raysYamamoto, Shunya; Sugimoto, Masaki; Miyashita, Atsumi; Hakoda, Teruyuki; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Mori, Toshiyuki*
no journal, ,
Platinum modified with cerium oxide (Pt-CeO ) is considered as promising cathode materials for use in polymer membrane electrolyte fuel cells. A key process to make this active is formation of highly dispersed Pt nanoparticles on a CeO
) is considered as promising cathode materials for use in polymer membrane electrolyte fuel cells. A key process to make this active is formation of highly dispersed Pt nanoparticles on a CeO surface. Therefore, there is a strong motivation for us to use this radiation technique for precipitation of the Pt nanoparticles on CeO
surface. Therefore, there is a strong motivation for us to use this radiation technique for precipitation of the Pt nanoparticles on CeO films, which would be expected to be a model electrocatalyst of Pt-CeO
films, which would be expected to be a model electrocatalyst of Pt-CeO . We deposited the CeO
. We deposited the CeO films on a SiO
films on a SiO substrate by magnetron sputtering. The CeO
substrate by magnetron sputtering. The CeO films in an aqueous solution containing H
films in an aqueous solution containing H PtCl
PtCl and C
and C H
H OH were irradiated with 2 MeV electron beams and
OH were irradiated with 2 MeV electron beams and  Co
Co  -rays at 50 kGy at maximum. The detailed analysis revealed homogeneous precipitation of metallic Pt by the irradiation with both the radiations, suggesting high applicability of the radiation-induced precipitation method to the preparation of the model Pt-CeO
-rays at 50 kGy at maximum. The detailed analysis revealed homogeneous precipitation of metallic Pt by the irradiation with both the radiations, suggesting high applicability of the radiation-induced precipitation method to the preparation of the model Pt-CeO electrocatalysts.
electrocatalysts.
 Co
Co  -ray
-rayYamamoto, Shunya; Shimada, Akihiko; Miyashita, Atsumi; Hakoda, Teruyuki
no journal, ,
Platinum (Pt) and Palladium (Pd) have been used in solid-state hydrogen sensors as a catalysis which acts to dissociate hydrogen molecules into protons and electrons. To apply solid-state hydrogen sensors under  -ray radiation, it is essential to understand the effects of
-ray radiation, it is essential to understand the effects of  -ray radiation on crystal structure of Pt and Pd. Rutherford backscattering spectrometry (RBS) combined with channeling has been used to examine crystal structure and composition of surface region. Thus, preparation of epitaxal films which can be analysis by RBS/channeling allow us to understand the influence of
-ray radiation on crystal structure of Pt and Pd. Rutherford backscattering spectrometry (RBS) combined with channeling has been used to examine crystal structure and composition of surface region. Thus, preparation of epitaxal films which can be analysis by RBS/channeling allow us to understand the influence of  -ray radiation on structure of the thin films. In the present study, epitaxial Pt and Pd films were grown on sapphire substrates by an rf magnetron sputtering. The crystallographic orientation and surface chemical states were characterized by X-ray diffraction and X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS). RBS/channeling analysis was performed to characterize the epitaxial films by employing He ions with the energy of 2.0 MeV. The epitaxial films were irradiated with
-ray radiation on structure of the thin films. In the present study, epitaxial Pt and Pd films were grown on sapphire substrates by an rf magnetron sputtering. The crystallographic orientation and surface chemical states were characterized by X-ray diffraction and X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS). RBS/channeling analysis was performed to characterize the epitaxial films by employing He ions with the energy of 2.0 MeV. The epitaxial films were irradiated with  Co
Co  -ray (
-ray ( 5 MGy) at RT in a sealed glass vessel in the air. The results of RBS and XPS suggest that enhanced oxidation of Pd films is related to nitric acid in air produced by
5 MGy) at RT in a sealed glass vessel in the air. The results of RBS and XPS suggest that enhanced oxidation of Pd films is related to nitric acid in air produced by  -ray radiation.
-ray radiation.
Sakaki, Hironao
no journal, ,
With the development of ultrashort-pulse high intensity laser systems and laser-handling techniques, a focused intensity becomes amount of light that reaches over 10 W/cm
W/cm . The laser is mainly applied to the study of a strong-electromagnetic field produced by laser-plasma interactions. We study this strong-electromagnetic field for a heavy-ion beam generation and acceleration (laser-driven ion acceleration) that show a particular property of laser-plasma interactions. It demonstrated by the laser irradiation with the intensity of 1
. The laser is mainly applied to the study of a strong-electromagnetic field produced by laser-plasma interactions. We study this strong-electromagnetic field for a heavy-ion beam generation and acceleration (laser-driven ion acceleration) that show a particular property of laser-plasma interactions. It demonstrated by the laser irradiation with the intensity of 1 10
10 W/cm
W/cm on the metal foil target. And, we measured highly-charge-state Fe ions accelerated up to 0.9 GeV are demonstrated with a 200 TW femtosecond high-intensity laser irradiating a micron-thick Al foil with Fe impurity on the surface. An energetic high-density beam of heavy ions with a large charge-to-mass ratio can be obtained, which is useful for many applications, such as a new-type heavy ion source.
on the metal foil target. And, we measured highly-charge-state Fe ions accelerated up to 0.9 GeV are demonstrated with a 200 TW femtosecond high-intensity laser irradiating a micron-thick Al foil with Fe impurity on the surface. An energetic high-density beam of heavy ions with a large charge-to-mass ratio can be obtained, which is useful for many applications, such as a new-type heavy ion source.
Kimata, Tetsuya*; Kato, Sho*; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Yamamoto, Shunya; Hakoda, Teruyuki; Kobayashi, Tomohiro*; Terai, Takayuki*
no journal, ,
Platinum (Pt) nanoparticles having high activities for an oxygen reduction reaction have been studied intensively for applications to polymer electrolyte fuel cells. We prepared the Pt nanoparticles on a glassy carbon (GC) substrate irradiated with 380 keV Ar at the fluence of 1.0
at the fluence of 1.0 10
10 ions/cm
ions/cm , and then analyzed their electrocatalytic properties by a rotating disk electrode method. The Pt nanoparticles on the Ar-ion-irradiated GC substrate exhibited ca. 2.5 times higher current density than those on the non-irradiated one. This striking result suggests that the Ar-ion-induced modification of the GC substrate would improve the electrocatalytic activities of the deposited Pt nanoparticles.
, and then analyzed their electrocatalytic properties by a rotating disk electrode method. The Pt nanoparticles on the Ar-ion-irradiated GC substrate exhibited ca. 2.5 times higher current density than those on the non-irradiated one. This striking result suggests that the Ar-ion-induced modification of the GC substrate would improve the electrocatalytic activities of the deposited Pt nanoparticles.